Glossary of Terms Used in Combinatorial
Chemistry
[A-B]
[C] [D] [E-G]
[H-K] [L]
[M-N] [O-P] [Q] [R]
[S] [T] [U-Z]
A-B
Analytical
Construct: Tool for development of chemistry on solid
support whereby the desired compound is prepared in a form which
facilitates analysis. This may be achieved by the insertion of an additional,
orthogonal linker
between the solid support and the standard linker thus allowing release
of the linker-bound compound at any desired point in compound assembly1-3.
Aptamer:
Oligonucleotide which displays specific binding to a protein or other
target, often selected by an iterative cycle of affinity-based enrichment4-6.
See also SELEX.
ArgoGel:
(Trademark of Argonaut Technologies, San Carlos, California, U.S.A.)
Beaded solid support with a crosslinked
polystyrene core and grafted linear poly(ethylene
glycol) (PEG) chains with terminal functional groups 7.
Array
Synthesis: Form of parallel
synthesis in which the reaction vessels are maintained in a
specified spatial distribution, e.g. the wells of a 96-well plate or
pins held in a rack 8-10.
Assay
Equivalent: An aliquot of a library
which will allow the library to be screened in a single assay. Particularly
applicable to libraries prepared by split/pool
procedure where it pertains to the number of particles required to sample
a library. Generally consists of a specified number of library
equivalents. For statistics related to this see ref. 11.
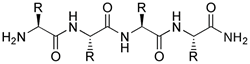
Backbone:
A scaffold of approximately linear
configuration. Thus in the generic
structure of a tetrapeptide shown below, the repeating polyamide
core structure (everything except for the R groups — see residue)
constitutes the backbone.
Bead:
(normally spherical) particle of solid
support.
Biased
Library: see Directed Library
Binning:
Approach to classifying the diversity of a set of compounds by grouping
related members in "bins" on the basis of common physical
or structural features. Commonly applied to the analysis of a set for
the completeness of coverage of the desired property
space 12.
Binary
Code: Relationship between a set of tags
and their corresponding ligands where building
block identity is denoted by the presence or absence
of a given tag or set of tags (i.e. the two "bits" 1 and 0).
Compare quantitative or ratio coding
13.
Building
Block: One of a number of interchangeable reagents which can be
used in combinatorial library
synthesis, part of the structure of which becomes incorporated into
the final product, i.e. its residue.
See also diversity reagent.

